Misc
Have Combustion Vehicle Sales Already Peaked?

Have Combustion Vehicle Sales Already Peaked?
Electric vehicle (EV) sales have grown rapidly over the past few years, but have they managed to make a dent in the global market?
To find out, we’ve visualized data from BloombergNEF that breaks down annual vehicle sales by three categories:
- Internal combustion (including traditional hybrids)
- Plug-in hybrids
- Battery electric
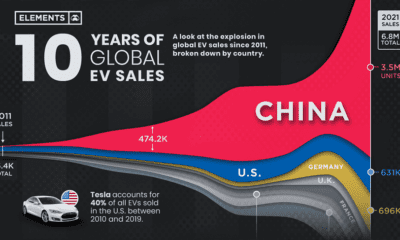
From this, we can see that EVs are definitely building up market share. In fact, combustion vehicle sales appear to have peaked in 2017.
Growth in EV Market Share
The following table lists global EV sales, as well as their relative market share.
| Year | EV Sales | EV Market Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 206,000 | 0.2 |
| 2014 | 320,000 | 0.4 |
| 2015 | 543,000 | 0.6 |
| 2016 | 791,000 | 0.9 |
| 2017 | 1,262,000 | 1.3 |
| 2018 | 2,082,000 | 2.2 |
| 2019 | 2,276,000 | 2.5 |
| 2020 | 3,244,000 | 4.2 |
| 2021 | 6,768,000 | 8.3 |
| 2022 | 10,522,000 | 13.0 |
*Includes plug-in hybrids. Source: EV Volumes
We can see that EV sales really picked up steam around 2019. This is likely due to various government subsidies and a growing list of models to choose from.
EV ranges, once a major limiting factor, are also becoming less of a concern as battery technology improves and more charging stations become available.
Will Combustion Vehicle Sales Stage a Comeback?
It seems unlikely that combustion vehicles will be able to reclaim much of their lost market share.
China, the world’s largest car market, is leading the world in terms of EV adoption. As of 2022, one in four new cars sold in the country is electric. The U.S. and EU are transitioning slower, but should catch up thanks to government subsidies and a planned phase-out of fossil fuel vehicles.
In the EU, the sale of new internal combustion vehicles will be banned by 2035. However, an exemption was recently made on behalf of Germany to allow the sale of cars that run on synthetic fuels.
In the U.S., the 13 states that adhere to California’s Zero Emissions Vehicle (ZEV) Program are aiming for 100% of cars sold in 2035 to be ZEVs. These states include California, Colorado, Connecticut, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Minnesota, New Jersey, New York, Oregon, Rhode Island, Vermont, and Washington.
Politics
How Do Chinese Citizens Feel About Other Countries?
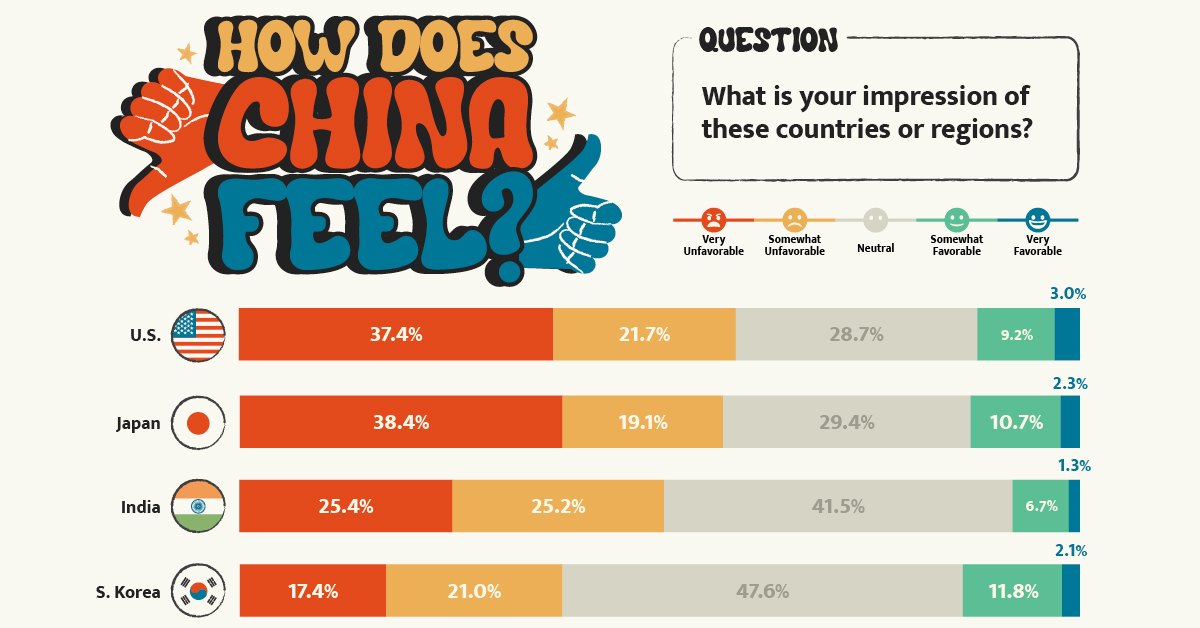
What is the Chinese public’s view of world powers? This visual breaks down Chinese sentiment towards other countries.
Public Opinion: How Chinese Citizens Feel About Other Countries
Tensions over Taiwan, the COVID-19 pandemic, trade, and the war in Ukraine have impacted Chinese sentiment towards other countries.
This visualization uses data from the Center for International Security and Strategy (CISS) at Tsinghua University to rank survey responses from the Chinese public on their attitudes towards countries and regions around the world.
Chinese Sentiment Towards Other Countries in 2023
In the Center’s opinion polls, which surveyed a random sample of more than 2,500 Chinese mainland adults in November 2022, Russia came out significantly ahead.
Just under 60% of respondents held Russia in a favorable view, with 19% seeing the country as “very favorable.” Contrast that to the mere 12% that viewed the U.S. in a positive light.
Here’s a closer look at the data. The percentages refer to the share of respondents that voted for said category.
| Country/Region | Very Unfavorable | Somewhat Unfavorable | Neutral | Somewhat Favorable | Very Favorable |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 United States | 37.4% | 21.7% | 28.7% | 9.2% | 3.0% |
| 🇯🇵 Japan | 38.4% | 19.1% | 29.4% | 10.7% | 2.3% |
| 🇮🇳 India | 25.4% | 25.2% | 41.5% | 6.7% | 1.3% |
| 🇰🇷 South Korea | 17.4% | 21.0% | 47.6% | 11.8% | 2.1% |
| 🇪🇺 European Union | 9.3% | 15.6% | 57.6% | 14.1% | 3.3% |
| Southeast Asia | 7.1% | 13.1% | 59.5% | 16.8% | 3.5% |
| 🇷🇺 Russia | 3.0% | 4.8% | 33.7% | 39.4% | 19.0% |
Japan ranked just below the U.S. in terms of overall unfavorability, though a slightly higher share of respondents saw Japan as “very unfavorable” compared to America. This is likely due to both modern tensions in the East China Sea over mutually claimed islands and historical tensions over the Sino-Japanese Wars.
Chinese sentiment towards India was also unfavorable at just over 50%, though notably the country also received the lowest favorability rating at just 8%.
Additional Survey Findings
The survey also found that 39% of Chinese people get their information on international security from Chinese state-run media (mainly through TV), with an additional 19% getting information from government websites and official social accounts. Conversely, only 1.7% get their news from foreign websites and foreign social media, partially due to the Great Firewall.
When asked about different international security issues, the biggest shares of Chinese citizens ranked the following as their top three:
- Pandemics (12.9%)
- Disputes over territory and territorial waters (12.9%)
- China-U.S. relations (12.0%)
The pandemic’s high score reflects the harsher impact COVID-19 had on China. Chinese borders were shut for years and the public faced intense measures to reduce spread.
In terms of other world events, the majority of Chinese people align with a more “Eastern” viewpoint. For example, in regards to the war in Ukraine, the report found that:
“About 80 percent of the respondents believe the U.S. and Western countries should be held most accountable [for the war], while less than ten percent of the respondents argue that Russia is mainly responsible.”– Center for International Security and Strategy, Tsinghua University
Overall, the views of the Chinese public reflect the opposite of those found in many Western countries. They provide an important insight that it is not just the Chinese government holding particular views about the world, but the Chinese public as well.
-

 Markets3 weeks ago
Markets3 weeks agoHow Big is the Market for Crude Oil?
-
 Maps6 days ago
Maps6 days agoMapped: The Safest Cities in the U.S.
-
 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Profitable U.S. Companies, by Sector
-

 apps5 days ago
apps5 days agoHow Long it Took for Popular Apps to Reach 100 Million Users
-
 Markets4 weeks ago
Markets4 weeks agoThe World’s Biggest Mutual Fund and ETF Providers
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoBrand Reputations: Ranking the Best and Worst in 2023
-
 Green5 days ago
Green5 days agoHotter Than Ever: 2023 Sets New Global Temperature Records
-
 Datastream4 weeks ago
Datastream4 weeks agoCan You Calculate Your Daily Carbon Footprint?