Green
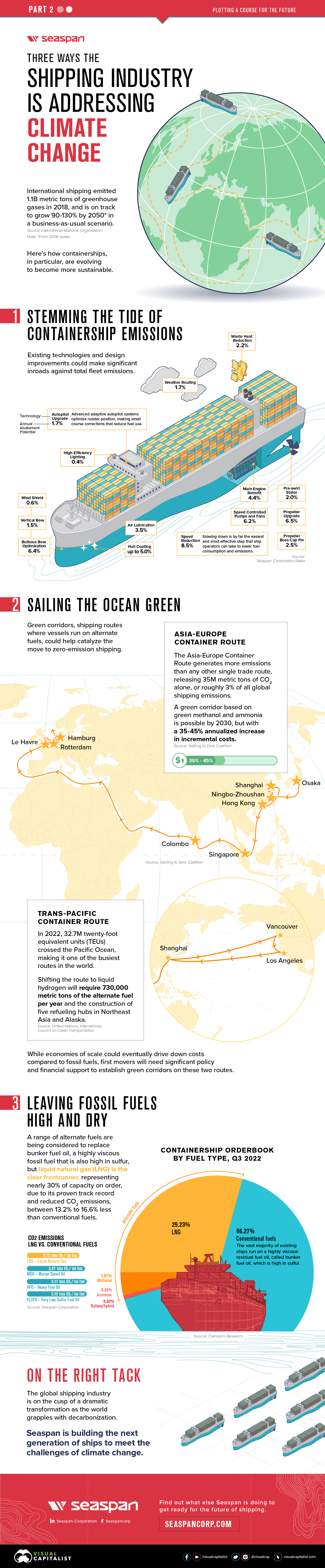
Chart: Automakers’ Adoption of Fuel-Saving Technologies
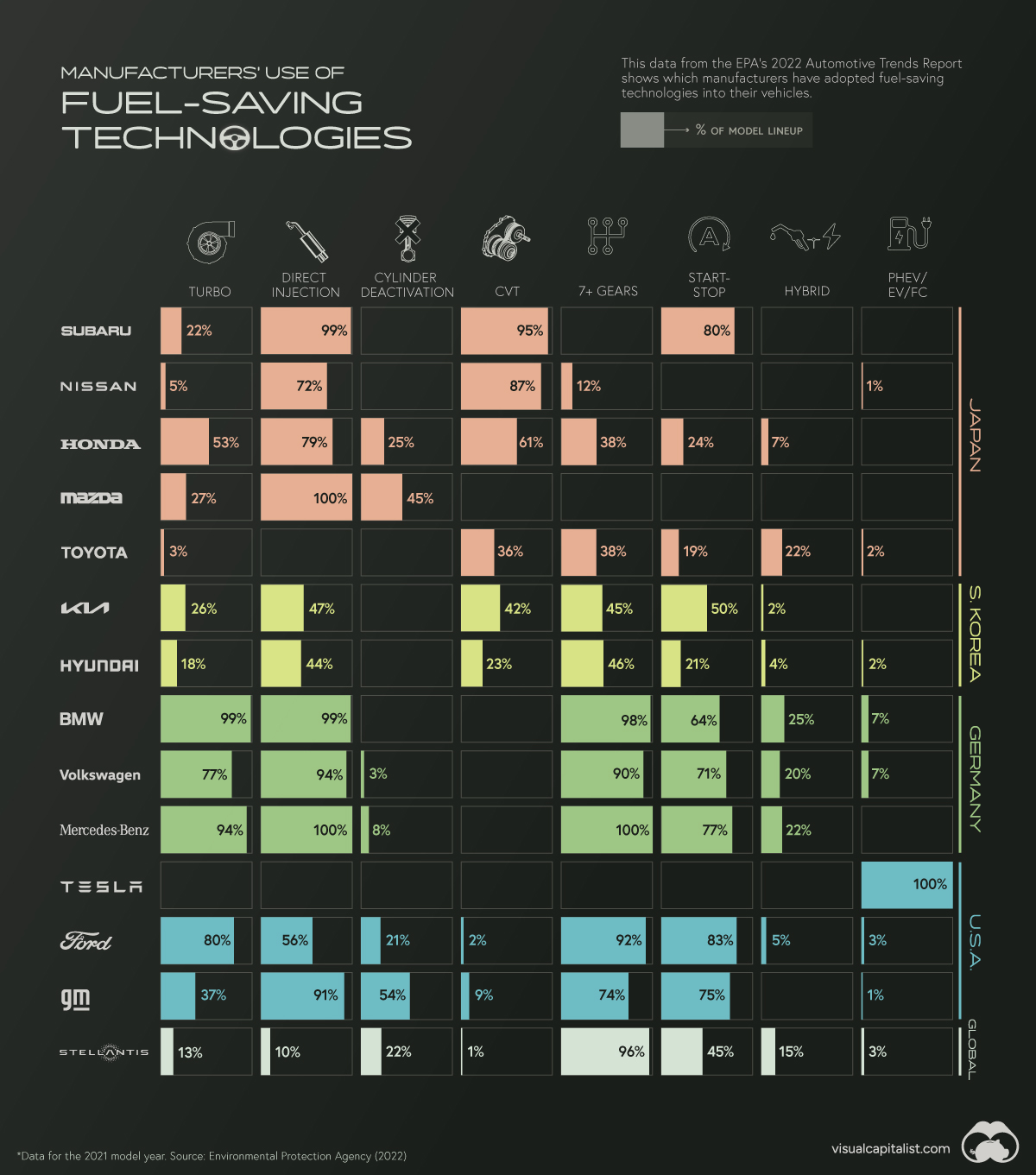
Automakers’ Adoption of Fuel-Saving Technologies
Over the past few decades, automakers have invested plenty of time and money into various fuel-saving technologies. This includes innovations such as direct injection, cylinder deactivation, and auto start-stop features.
Keeping track of which companies have adopted these technologies can be difficult. Thankfully, the EPA’s 2022 Automotive Trends Report includes data that shows which automakers have adopted what technologies.
Understanding the Data
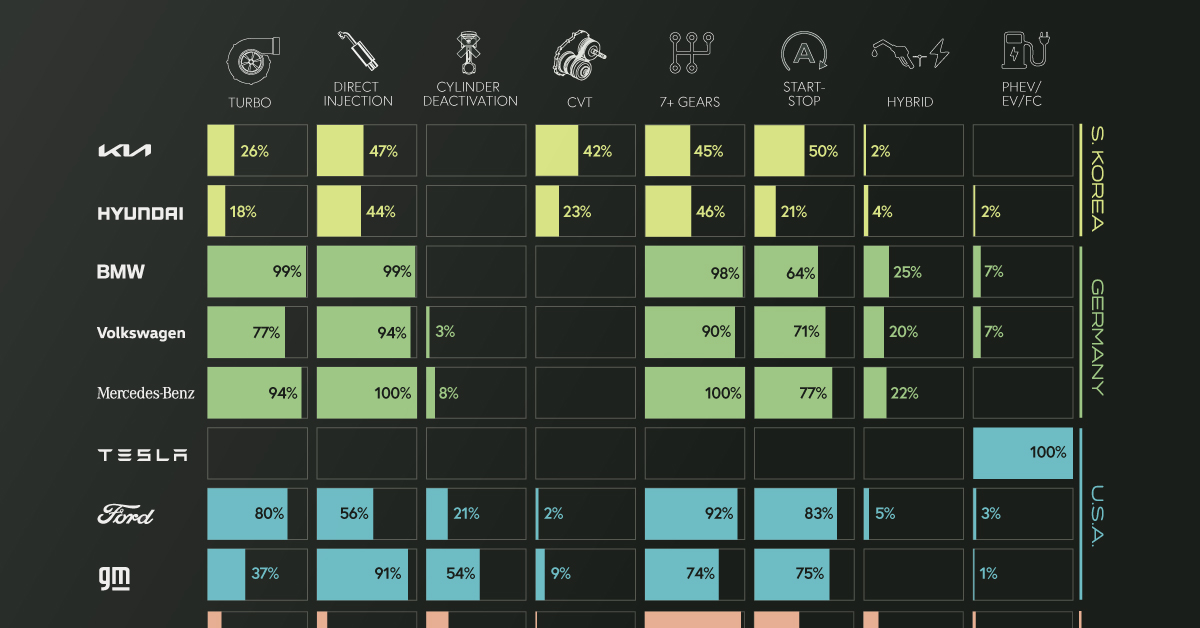
The percentages in this infographic show how 14 major automakers have adopted various fuel-saving technologies into their lineups. The report did not specify if this data is for North American models only.
| Brand | Turbo | Direct Injection | Cylinder Deact. | CVT | 7+ Gears | Start-Stop | Hybrid | PHEV/EV/FC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subaru | 22% | 99% | 0% | 95% | 0% | 80% | 0% | 0% |
| Nissan | 5% | 72% | 0% | 87% | 12% | 0% | 0% | 1% |
| Honda | 53% | 79% | 25% | 61% | 38% | 24% | 7% | 0% |
| Mazda | 27% | 100% | 45% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Toyota | 3% | 0% | 0% | 36% | 38% | 19% | 22% | 2% |
| Kia | 26% | 47% | 0% | 42% | 45% | 50% | 2% | 0% |
| Hyundai | 18% | 44% | 0% | 23% | 46% | 21% | 4% | 2% |
| BMW | 99% | 99% | 0% | 0% | 98% | 64% | 25% | 7% |
| Volkswagen | 77% | 94% | 3% | 0% | 90% | 71% | 20% | 7% |
| Mercedes-Benz | 94% | 100% | 8% | 0% | 100% | 77% | 22% | 0% |
| Tesla | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 100% |
| Ford | 80% | 56% | 21% | 2% | 92% | 83% | 5% | 3% |
| GM | 37% | 91% | 54% | 9% | 74% | 75% | 0% | 1% |
| Stellantis | 13% | 10% | 22% | 1% | 96% | 45% | 15% | 3% |
There are several geographical trends hidden within this dataset. To make them more obvious, we color-coded the 14 automakers by their nationality.
Asian Automakers
Starting from the top of the graphic, we can see that Japanese automakers are big proponents of gasoline direct injection (GDI) engines, as well as continuously variable transmissions (CVT).
With a GDI engine, fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber at high pressure. This is more precise than the traditional method known as port injection, which results in greater fuel efficiency and lower emissions.
CVT transmissions use pulleys instead of gears to improve fuel efficiency. CVTs are best paired with smaller, lower output engines, which may explain why Japanese automakers (who have a history of building smaller cars) have adopted them so widely.
Note that Toyota is listed as having 0% adoption of direct injection, but this isn’t exactly true. The automaker uses its D4-S system, which is a combination of both port and direct fuel injection.
South Korean automakers, on the other hand, have a more balanced technology profile, adopting a wider number of technologies, but each to a lesser degree.
German Automakers
German automakers are well-known for their expertise in building combustion engines, so it’s no surprise they use turbocharging and direct injection in nearly every model.
They’ve also heavily adopted high gear-count transmissions (7 or more gears), which can not only enable better fuel efficiency, but also faster acceleration. The downside to these transmissions is that they can be very heavy and complex.
Furthermore, German automakers utilize the auto start-stop feature in many of their vehicles, and are tied with Toyota in terms of hybrid adoption.
American & Other Automakers
Ford and GM’s technology profile is similar to the Germans, using turbocharging and direct injection combined with 7+ gear transmissions.
GM uses turbocharging less frequently, but stands out with its high usage of cylinder deactivation technology, at 54% of models. Referred to by GM as Active Fuel Management (AFM), this feature shuts down half of the engine’s cylinders during light driving.
GM is known for its small-block V8 engines, which can be had in many of the company’s models. Given the high cylinder count of a V8, AFM is a clever trick for improving fuel efficiency.
Stellantis, which is a merger between Italian-American Fiat Chrysler and French Peugeot, has not widely adopted many technologies except for the 7+ gear transmission.
Finally there’s Tesla, which does not use any of the aforementioned technologies due to it being a pure electric automaker.
Going The Way of the Dinosaur
The technologies shown in this infographic have helped to bring the average mpg of a new car to record highs in recent years.
Many of these innovations could become obsolete as automakers slowly phase out gasoline engines. In 2021, six major automakers including Ford, Mercedes-Benz, and GM pledged to phase out the sale of new gasoline and diesel-powered cars by 2040.
Other companies such as Porsche believe that the combustion engine still has a future, pointing to synthetic fuels as a means of significantly reducing CO2 emissions.
shipping
3 Ways the Shipping Industry is Addressing Climate Change
The shipping industry is responsible for 2.89% of all carbon emissions. Here are three ways it could evolve to address climate change.
3 Ways the Shipping Industry is Addressing Climate Change
The global shipping industry is on the verge of a transformation not seen since the transition from sail to steam.
In 2018, the industry emitted 1.1 billion metric tons of greenhouse gas emissions, representing 2.89% of all anthropogenic, or human-caused, emissions. And according to the International Maritime Organization (IMO) that could increase 90-130% in 2050, from a 2008 baseline.
This is the second and final part of The Shipping Industry: Plotting a Course for the Future, a two-part series from our sponsor Seaspan Corporation, that looks at three ways that containerships in particular, could evolve to become more sustainable.
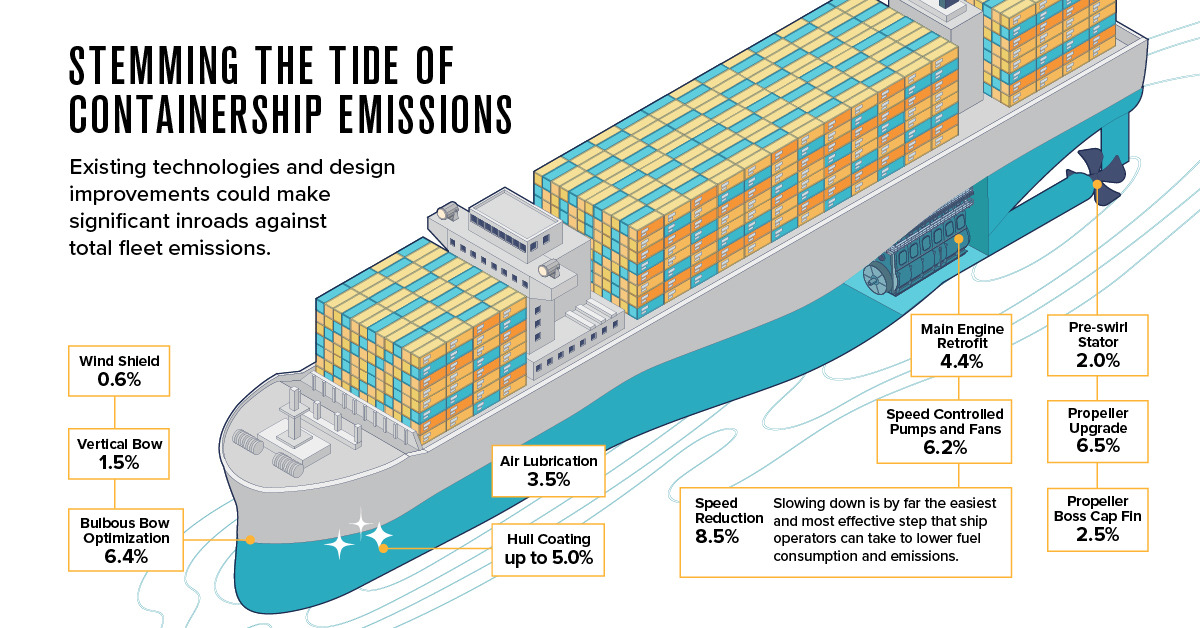
1. Stemming the Tide of Containership Emissions
Unlike personal transport, which has a proven and commercially scalable technology in electric vehicles, there’s no silver bullet for shipping. However, existing technologies and design improvements could help make significant inroads against total fleet emissions.
According to data from Seaspan, propeller upgrades (6.5%), hull coatings (up to 5.0%), and main engine retrofits (4.4%) won’t bring emissions to zero on their own, but taken together they add up to big savings.
| Technology | Annual Abatement potential |
|---|---|
| Speed reduction | 8.5% |
| Propeller Upgrade | 6.5% |
| Bulbous bow optimization | 6.4% |
| Speed Controlled Pumps and Fans | 6.2% |
| Hull coating | 5.0% (up to) |
| Main engine retrofit | 4.4% |
| Air lubrication | 3.5% |
| Propeller boss cap fin | 2.5% |
| Waste Heat Reduction | 2.2% |
| Pre-swirl stator | 2.0% |
| Weather Routing | 1.7% |
| Autopilot Upgrade | 1.7% |
| Vertical bow | 1.5% |
| Wind shield | 0.6% |
| High-Efficiency Lighting | 0.4% |
Interestingly, the biggest potential impact could come from slowing down ships (8.5%), which lowers fuel consumption and as a consequence, emissions. In the race to net zero, slow and steady could very well win the race.
2. Sailing the Ocean Green
In the long run, though, design tweaks don’t address the elephant seal in the room, which is the industry’s reliance on fossil fuels. Ships that run on alternate fuels, like ammonia, methanol, and even wind-power, are all in development, but many of the technologies are still in the early stages.
To help spur development, a group of countries at COP26, the annual UN climate conference, committed to establishing green shipping corridors where vessels would run on alternate fuels. A total of 24 countries signed the Clydebank Declaration, including the U.S. and the UK, and together they hope to catalyze the shift to zero emission shipping.
3. Leaving Fossil Fuels High and Dry
Many ship owners and operators are looking at Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) as a transitional fuel, while alternate fuel technologies mature. LNG emits between 13.2% and 16.6% less CO2 than conventional bunker fuel oil, a highly viscous residual fuel that is high in sulfur, so it’s no surprise that LNG-powered containerships represent 29.23% of the existing orderbook.
But with all but 2.4% of the current global fleet running on fossil fuels, there is still a long journey ahead.
On the Right Tack
The 1997 Kyoto Protocol established the IMO as the forum for climate change action for the shipping industry, which many have criticized for not moving fast and far enough on climate change.
At the July 2023 meeting of the Marine Environment Protection Committee, the IMO adopted a new greenhouse gas strategy, which set “indicative checkpoints” for emission reductions for 2030 and 2040 in place of binding targets, and committed to hit net zero “by or around, i.e. close to 2050, taking into account different national circumstances.” The IMO also declined to put a price on carbon.
Even without firm targets, many industry players aren’t waiting to move on the climate emergency. Seaspan, the world’s largest independent charter owner and manager of containerships, is moving to green their fleet. They recently signed an agreement to retrofit 15 ships with dual-fuel engines that can also run on green methanol, with an option for 45 more.

Find out what else Seaspan is doing to get ready for the future of shipping.

-
 shipping6 months ago
shipping6 months agoCharted: The Dipping Cost of Shipping
After a dramatic spike during the pandemic, shipping costs have now fallen back to Earth. What does that mean for shippers and the economy?
-
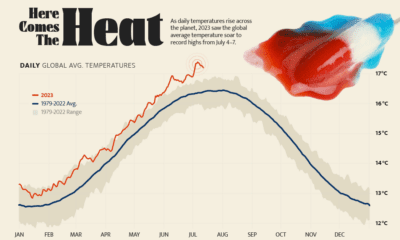
 Environment5 days ago
Environment5 days agoHotter Than Ever: 2023 Sets New Global Temperature Records
-
 Datastream4 weeks ago
Datastream4 weeks agoCan You Calculate Your Daily Carbon Footprint?
-
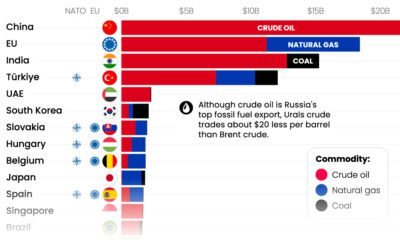
 Energy2 weeks ago
Energy2 weeks agoWho’s Still Buying Russian Fossil Fuels in 2023?
-

 VC+4 days ago
VC+4 days agoWhat’s New on VC+ in July
-
 Investor Education4 weeks ago
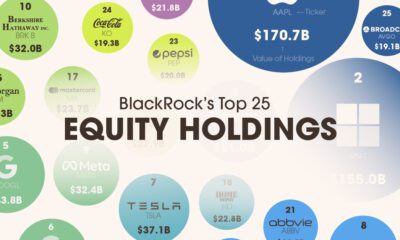
Investor Education4 weeks agoVisualizing BlackRock’s Top Equity Holdings
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoMeet the Competing Apps Battling for Twitter’s Market Share
-
 Politics15 hours ago
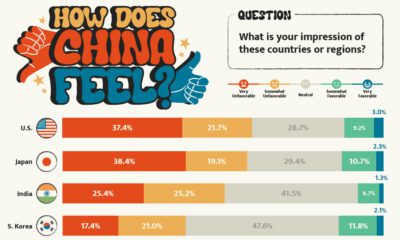
Politics15 hours agoHow Do Chinese Citizens Feel About Other Countries?
-
 Markets4 weeks ago
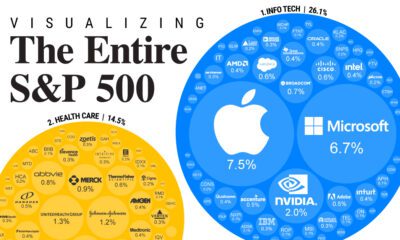
Markets4 weeks agoVisualizing Every Company on the S&P 500 Index