Business
Visualizing Tech Company Layoffs in 2022
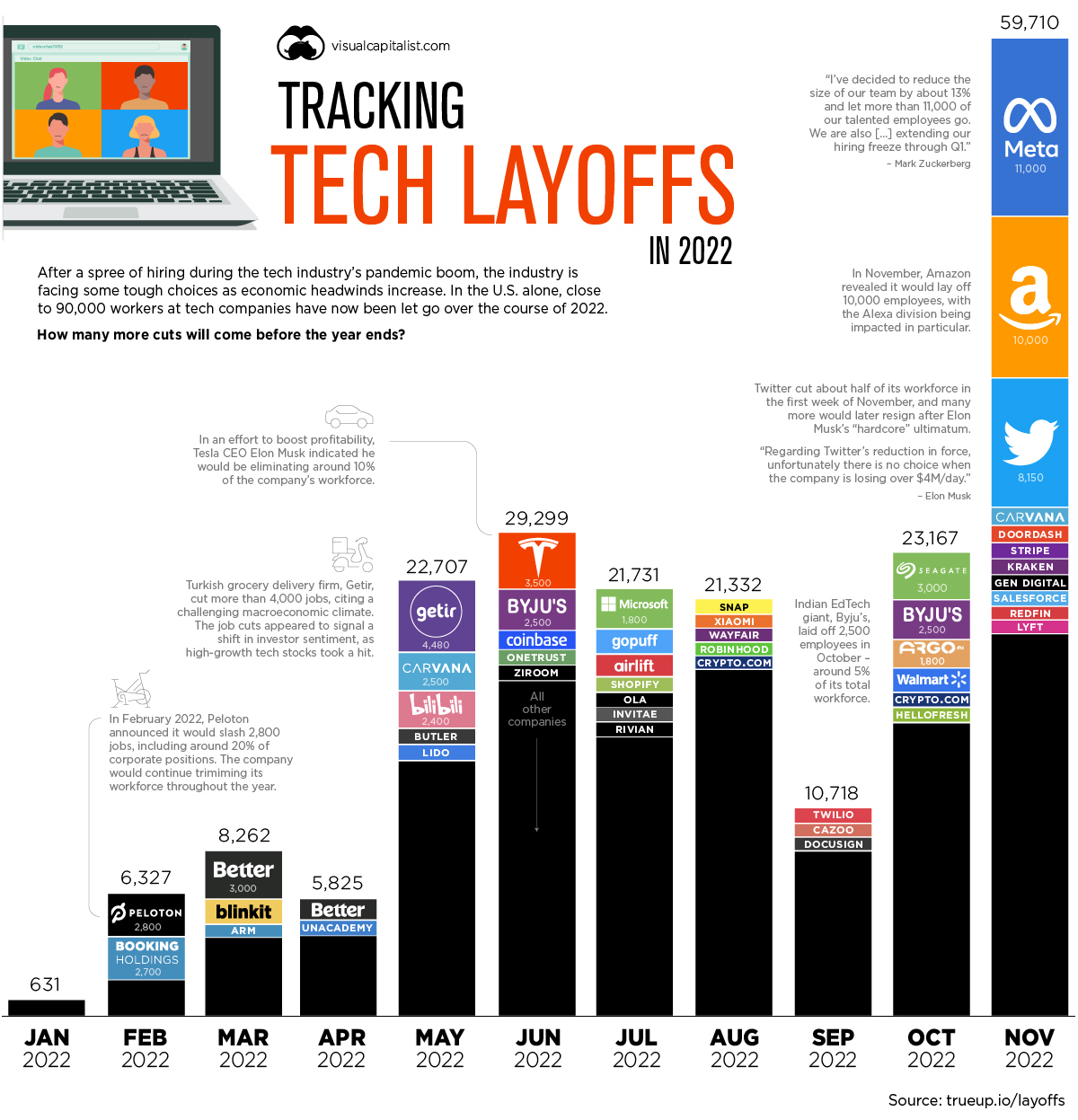
Visualizing Tech Company Layoffs in 2022
Layoffs are happening so frequently in 2022 that everyone from Crunchbase to Indian tech website Inc42 are now keeping track.
There is even a standalone website tracking all tech layoffs in the United States.
For the purposes of this infographic, we’ve used data from trueup.io which includes a mix of U.S. and international tech companies that have let workers go in 2022.
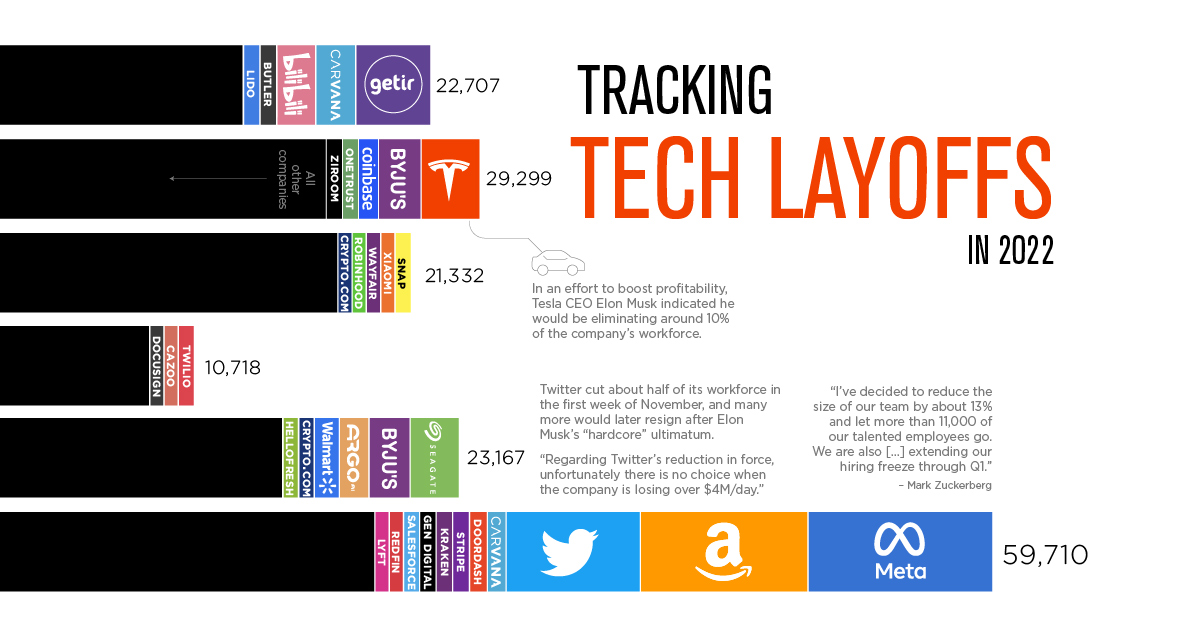
A Thousand Cuts: Mass Layoffs by Tech Companies
Layoffs are having an impact on the entire tech industry, and the phenomenon is global. Here are some of the most high-profile examples of mass layoffs in 2022:
Meta: The social media giant faces competition from upstarts like TikTok, as well as a pool of ad dollars that is shrinking in the face of a faltering economy. Although this reduction in headcount is painful for Meta, it’s worth considering a more broad perspective. In close to two decades of doing business, these will be the company’s first wide-scale job cuts.
Twitter: Though Meta wins with sheer volume of cuts, Twitter’s mass layoffs are surely the most dramatic. In early November, the company’s iconoclastic new owner, Elon Musk, slashed 50% of the workforce, and soon after, thousands of contractors also suddenly lost their jobs. Estimating how many employees remain at the company will remain a challenge until the dust settles.
Byju’s: Layoffs are not just confined to the United States. India’s sizable tech sector is also facing cuts. EdTech giant, Byju’s, laid off 2,500 employees in October—around 5% of its total workforce.
Peloton: The high-end workout equipment company has been dropping its headcount throughout the year. In the visualization above, companies like Meta stand out as they eliminated thousands of employees all at once. Peloton, however, executed its layoffs in stages throughout the year. After strong growth during the pandemic began to stagnate, the company is slimming down to regain profitability.
Why are Tech Companies Laying Off so Many People?
The stated reasons for letting so many workers go are economic uncertainty (external factors) and poor performance (internal factors).
Goldman Sachs Research points out that “higher interest rates and tighter financial conditions disproportionately impact the sector because tech company profits are typically expected further out in the future and therefore subject to greater duration risk.”
Shrinking advertising budgets and the implosion of the cryptocurrency market are also factors that may have influenced the decision to cut headcounts. Twitter and Snapchat fall into the former bucket, while Coinbase and Kraken fall into the latter.
What Do These Job Cuts Mean for the Economy?
At face value, widespread layoffs in the tech sector might appear to be a bad omen for the wider economy—especially given the outsize influence tech companies have on the markets.
Thankfully, this does not appear to be the case. Payroll and wage data from the U.S. government have exceeded expectations, and the country’s unemployment rate is close to a half-century low.
So, why the disconnect?
First off, tech jobs only account for less than 3% of total employment in America. As well, tech workers who’ve lost their jobs have a high likelihood of securing a new job in short order.
It remains to be seen whether November will be the peak of job cuts. Employers generally try to avoid letting people go right before the holiday season. One week into December, Trueup.io has tracked 7,600 more layoffs.
Markets
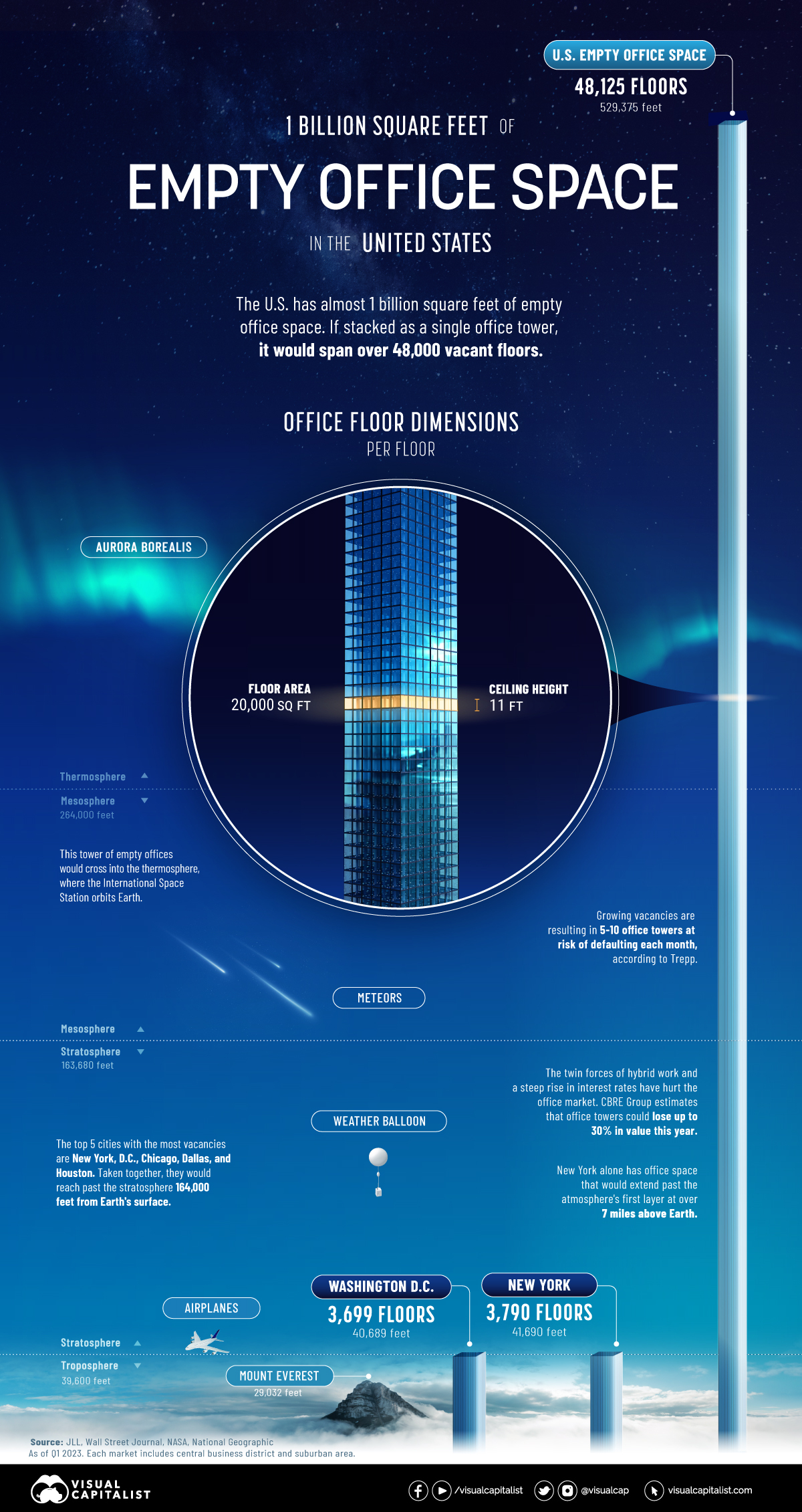
Visualizing 1 Billion Square Feet of Empty Office Space
Empty office space is hitting record highs in 2023. We show almost 1 billion square feet of unused space stacked as a single office tower.

1 Billion Square Feet of Empty Office Space
In April, one of America’s largest office owners, Brookfield, defaulted on a $161 million loan.
The loan, covering 12 office buildings, was mainly concentrated in the Washington, D.C. market. Faced with low occupancy rates, it joined other office giants Blackstone and WeWork defaulting on office debt this year.
The above graphic shows nearly 1 billion square feet of empty office space in the U.S. based on data from JLL—and the wider implications of office towers standing empty.
Ranking U.S. Cities by Empty Office Space
At the end of the first quarter of 2023, a record 963 million square feet of office space was unoccupied in America. An estimated five to 10 office towers are at risk of defaulting each month according to Manus Clancy, senior managing director at Trepp.
Here are cities ranked by their total square feet of office vacancy as of Q1 2023. Figures include central business districts and suburban areas.
| Ranking | Market | Total Vacancy (SF) | Total Vacancy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | New York | 75.8M | 16.1% |
| 2 | Washington, D.C. | 74.0M | 20.8% |
| 3 | Chicago | 63.2M | 23.5% |
| 4 | Dallas | 53.5M | 25.0% |
| 5 | Houston | 49.3M | 25.6% |
| 6 | Los Angeles | 47.1M | 24.1% |
| 7 | New Jersey | 43.3M | 25.8% |
| 8 | Atlanta | 38.1M | 21.6% |
| 9 | Boston | 31.8M | 19.1% |
| 10 | Philadelphia | 27.8M | 18.8% |
| 11 | Denver | 27.3M | 21.6% |
| 12 | Phoenix | 25.2M | 23.9% |
| 13 | San Francisco | 22.8M | 26.4% |
| 14 | Seattle | 21.4M | 17.7% |
| 15 | Minneapolis | 19.9M | 19.7% |
| 16 | Detroit | 18.0M | 19.3% |
| 17 | Orange County | 17.7M | 17.6% |
| 18 | Salt Lake City | 13.9M | 18.5% |
| 19 | Kansas City | 13.8M | 20.8% |
| 20 | Pittsburgh | 13.8M | 21.8% |
| 21 | Charlotte | 13.7M | 20.6% |
| 22 | Austin | 13.6M | 18.9% |
| 23 | Baltimore | 13.1M | 18.2% |
| 24 | Portland | 12.8M | 17.5% |
| 25 | Silicon Valley | 12.1M | 17.3% |
| 26 | Oakland–East Bay | 11.7M | 22.0% |
| 27 | San Diego | 10.7M | 12.3% |
| 28 | St. Louis | 10.5M | 21.9% |
| 29 | Cincinnati | 10.1M | 21.4% |
| 30 | Sacramento | 9.9M | 19.6% |
| 31 | Fairfield County | 9.7M | 25.4% |
| 32 | Columbus | 9.7M | 21.7% |
| 33 | Milwaukee | 9.2M | 24.0% |
| 34 | Nashville | 9.0M | 18.9% |
| 35 | Raleigh-Durham | 8.9M | 15.2% |
| 36 | Indianapolis | 8.6M | 22.4% |
| 37 | Tampa | 8.2M | 17.2% |
| 38 | Fort Worth | 7.6M | 16.7% |
| 39 | Miami | 7.6M | 16.2% |
| 40 | Cleveland | 7.3M | 18.3% |
| 41 | San Antonio | 7.2M | 17.8% |
| 42 | Long Island | 6.3M | 15.2% |
| 43 | Westchester County | 5.8M | 22.1% |
| 44 | Jacksonville | 5.4M | 18.6% |
| 45 | Orlando | 5.0M | 13.3% |
| 46 | San Francisco Peninsula | 4.4M | 13.3% |
| 47 | Richmond | 4.3M | 13.3% |
| 48 | Fort Lauderdale | 4.3M | 16.1% |
| 49 | North San Francisco Bay | 4.0M | 18.3% |
| 50 | Louisville | 3.6M | 16.8% |
| 51 | Des Moines | 3.2M | 12.0% |
| 52 | Hampton Roads | 3.1M | 14.7% |
| 53 | West Palm Beach | 2.4M | 10.3% |
| 54 | Grand Rapids | 1.8M | 13.2% |
| United States | 962.5M | 20.2% |
Numbers may not total 100 due to rounding.
New York has roughly 76 million square feet of empty office space. If this were stacked as a single office building, it would stretch 7 miles into the atmosphere. In 2019, the office sector accounted for about a third of all jobs in the city.
Falling closely behind is Washington, D.C. with a 21% vacancy rate—8% higher than what is typically considered healthy. Occupiers are downsizing given remote work trends, yet some office buildings are being converted to residential properties, curtailing vacancy rates.
Across 54 markets in the dataset, San Francisco has the highest vacancy rate at over 26%. Prior to the pandemic, vacancy rates were about 4%. This year, Salesforce walked away from a 30-story tower in downtown San Francisco spanning 104,000 square feet in an effort to cut costs.
Overall, rising interest rates and higher vacancies have hurt U.S. office markets, with many cities potentially seeing an uptick in vacancies going forward.
Empty Office Space: Impact on Banks
Office building valuations are projected to fall 30% in 2023 according to Richard Barkham, global chief economist at CBRE Group.
A sharp decline in property values could potentially result in steep losses for banks. This is especially true for small and regional banks that make up the majority of U.S. office loans. Big banks cover roughly 20% of office and downtown retail totals.
Consider how commercial real estate exposure breaks down by different types of banks:
| Bank Assets | Commercial Real Estate Loans % of Total Assets | Share of Industry Assets |
|---|---|---|
| <$100M | 11.3% | 0.2% |
| $100M-$1B | 26.9% | 4.7% |
| $1B-$10B | 32.5% | 9.7% |
| $10B-$250B | 18.1% | 30.1% |
| >$250B | 5.6% | 55.5% |
Source: FitchRatings
For big banks, a recent stress test by the Federal Reserve shows that a 40% decline in commercial property values could result in a $65 billion loss on their commercial loan portfolios. The good news is that many big banks are sitting on healthy capital reserves based on requirements set in place after the global financial crisis.
Smaller banks are a different story. Many have higher loan concentrations and less oversight on reserve requirements. If these loan portfolios deteriorate, banks may face a downgrade in ratings and higher credit losses.
Additionally, banks with loans in markets with high vacancy rates like San Francisco, Houston, and Washington, D.C. could see more elevated risk.
How High Rates Could Escalate Losses
Adding further strain are the ramifications of higher interest rates.
Higher rates have negatively impacted smaller banks’ balance sheets—meaning they are less likely to issue new loans. This is projected to cause commercial real estate transaction volume to decline 27% in 2023, contributing to lower prices. Banks have already slowed lending for commercial real estate in 2023 due to credit quality concerns.
The good news is that some banks are extending existing loan terms or restructuring debt. In this way, banks are willing to negotiate new loan agreements to prevent widespread foreclosures from hurting their commercial loan portfolios. Short-term extensions on existing loans were often seen during the global financial crisis.
Still, foreclosures could take place if restructuring the loan doesn’t make financial sense.
Overall, only so many banks may be willing to wait out the uncertainty with loan extensions if fundamentals continue to worsen. Offices that are positioned to weather declines will likely have better quality, location, roster of tenants, and financing structures.
-
 Energy3 weeks ago
Energy3 weeks agoHow Old Are the World’s Nuclear Reactors?
-
 Maps7 days ago
Maps7 days agoMapped: World’s Top 40 Largest Military Budgets
-

 Energy3 weeks ago
Energy3 weeks agoHow Big is the Market for Crude Oil?
-
 Cities7 days ago
Cities7 days agoMapped: The Safest Cities in the U.S.
-
 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Profitable U.S. Companies, by Sector
-

 apps5 days ago
apps5 days agoHow Long it Took for Popular Apps to Reach 100 Million Users
-
 Markets4 weeks ago
Markets4 weeks agoThe World’s Biggest Mutual Fund and ETF Providers
-

 Brands2 weeks ago
Brands2 weeks agoBrand Reputations: Ranking the Best and Worst in 2023